What is LLM Serving?#
Large Language Model (LLM) serving refers to the process of deploying trained language models to production environments where they can handle user requests and generate responses in real-time. This is fundamentally different from training models - serving focuses on making models available, scalable, and performant for end users.
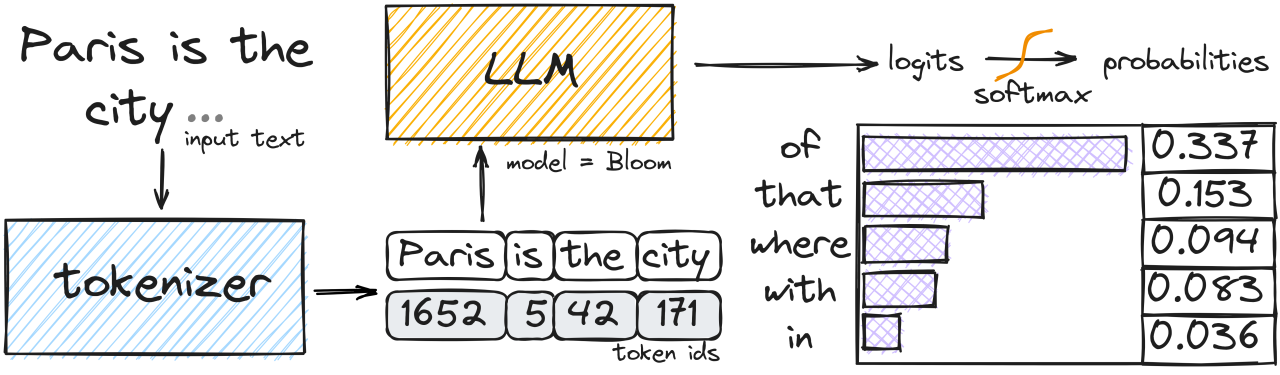
The LLM Text Generation Process#
LLMs operate as next-token predictors. Here’s how they work:
Tokenization: Input text is converted into tokens (words, subwords, or characters)
Processing: The model processes these tokens to understand context
Generation: The model generates output one token at a time
Completion: Generation stops when reaching stopping criteria or maximum length
Two Phases of LLM Inference#
LLM inference operates through two distinct phases that determine performance characteristics:
Prefill Phase#
The model encodes all input tokens simultaneously
High efficiency through parallelized computations
Maximizes GPU utilization
Precomputes and caches key-value (KV) vectors as intermediate token representations
Decode Phase#
The model generates tokens sequentially using the key-value cache (KV cache)
Each token depends on all previous tokens
Limited by memory bandwidth rather than compute capacity
Underutilizes GPU resources compared to prefill phase
|
|---|
prefill: parallel processing of prompt tokens, decode: sequential processing of single output tokens. |
